OSGI is a fundamental element in the technology stack of Adobe Experience Manager (AEM). It is used to control the bundles of AEM and their configuration.
OSGI bundles or components can be composed into an application and deployed and they can be stopped, installed, started individually. The interdependencies are handled automatically. Each OSGI Component is contained in one of the various bundles.
In the cases when you don't want to hardcode the values in the code eg. some host url or some parameter which is dynamic and can be changed frequently or the value which is different for each runmode of your aem instance, in those cases you use OSGI configuration.
By defining configuration values, you can define values used by an OSGI service and use these values while the service is running. Unlike hard-coding values in an AEM OSGI service, defining values in the AEM configMgr lets you change values without re-compiling the bundle.
You can manage the OSGI configuration settings for such bundles by :
Creating a OSGI Configuration service -
Use the below Java class example to create an osgi config service:
package com.foo.community.core;
import java.util.Map;
import org.apache.felix.scr.annotations.Activate;
import org.apache.felix.scr.annotations.Component;
import org.apache.felix.scr.annotations.Deactivate;
import org.apache.felix.scr.annotations.Modified;
import org.apache.felix.scr.annotations.Property;
import org.apache.felix.scr.annotations.Service;
import org.apache.sling.commons.osgi.PropertiesUtil;
import org.osgi.service.component.ComponentContext;
@Component(immediate=true, metatype=true)
@Service({MyConfig.class})
public class MyConfig
{
@Property(label="Sample Property", value={"property1"},
description="Sample property to demonstrate osgi config")
private static final String SAMPLE_PROPERTY = "sampleProperty";
private String sampleProperty;
public MyConfig() {}
public String getSampleProperty()
{
return sampleProperty;
}
@Activate
protected void activate(Map context)
{
sampleProperty = PropertiesUtil.toString(context
.get("sampleProperty"), "property1");
}
@Deactivate
protected void deactivate()
{
sampleProperty = null;
}
@Modified
protected void modified(ComponentContext context)
{
sampleProperty = PropertiesUtil.toString(context
.getProperties().get("sampleProperty"), "property1");
}
}
Notice that in the above code I have used SCR annotations to create a service but those annotations are deprecated now, so you can use OSGI annotations instead.To know more about scr annotations refer this page.
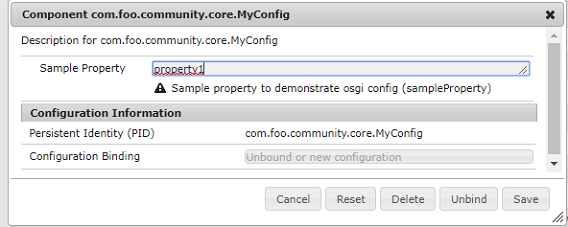
OSGi Configuration with the Web Console -
You can access the Configuration tab of the Web Console by:
http://localhost:4502/system/console/configMgr
then search for the MyConfig, you can see the config we created above as below:
OSGi Configuration with the Repository (CRX Nodes) -
To add the new configuration to the repository:
- Go to your project folder- /apps/<yourProject>, then create the config folder (sling:Folder):
config.<run-mode> - specific to a particular run mode
- Under this folder create a node:
Name: the persistent identity (PID)
for eg. in our case- com.foo.community.core.MyConfig
- For each parameter that you want to configure, create a property on this node:
Type: as appropriate.
Value: as required.
Below is the screenshot of the config I created for global and author runmode-
It's xml representation (com.foo.community.core.MyConfig.xml) is shown below:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<jcr:root xmlns:sling="http://sling.apache.org/jcr/sling/1.0"
xmlns:jcr="http://www.jcp.org/jcr/1.0"
jcr:primaryType="sling:OsgiConfig"
sampleProperty="Value edited from crx author"/>
Reading config values through Javascript Use-API:Use the below JS Use-API code snippet to use the config value and return to sightly-
var global = this;
use(function () {
if (global.sling && global.Packages) {
var myConfigService = global.sling.
getService(global.Packages.com.foo.community.core.MyConfig);
}
var sampleProperty = myConfigService.getSampleProperty();
return {
sampleProperty : sampleProperty
};
});
To read osgi config values through Java, refer this post.Resolution Order of the configurations-
Resolution Order at Startup-
The following order of precedence is used:
- Repository nodes under /apps/*/config of type sling:OsgiConfig.
- Repository nodes with type sling:OsgiConfig under /libs/*/config.
- Any .config files from <cq-installation-dir>/crx-quickstart/launchpad/config/ on local file system.
Resolution Order at Runtime-
Configuration changes made while the system is running trigger a reload with the modified configuration.
Then the following order of precedence applies:
- Modifying a configuration in the Web console will take immediate effect as it takes precedence at runtime.
- Modifying a configuration in /apps will take immediate effect.
- Modifying a configuration in /libs will take immediate effect.

No comments:
Post a Comment